Diabetes is an endemic pathology affecting ~ 380 million people worldwide. About 10% of them is affected by type 1 diabetes (T1D), the most severe form of the pathology type that requires periodical exogenous insulin injection. T1D patients are almost slave of their pathology due to the perform multiple injections and fingerpricks per day and to adhere to the therapy 365 days/year.
Artificial pancreas (AP) represents a technological solution aiming at continuously monitoring the patient’s blood glucose level and at automatically infusing insulin in the body. Current APs are external and inject insulin in the subcutaneous tissue. This imply limitations in the lifestyle and significant delays in the insulin adsorption kinetics.
The development of fully implantable AP is hampered, at present, by the need of periodic surgical operations to refill the insulin reservoir and to replace the implanted battery.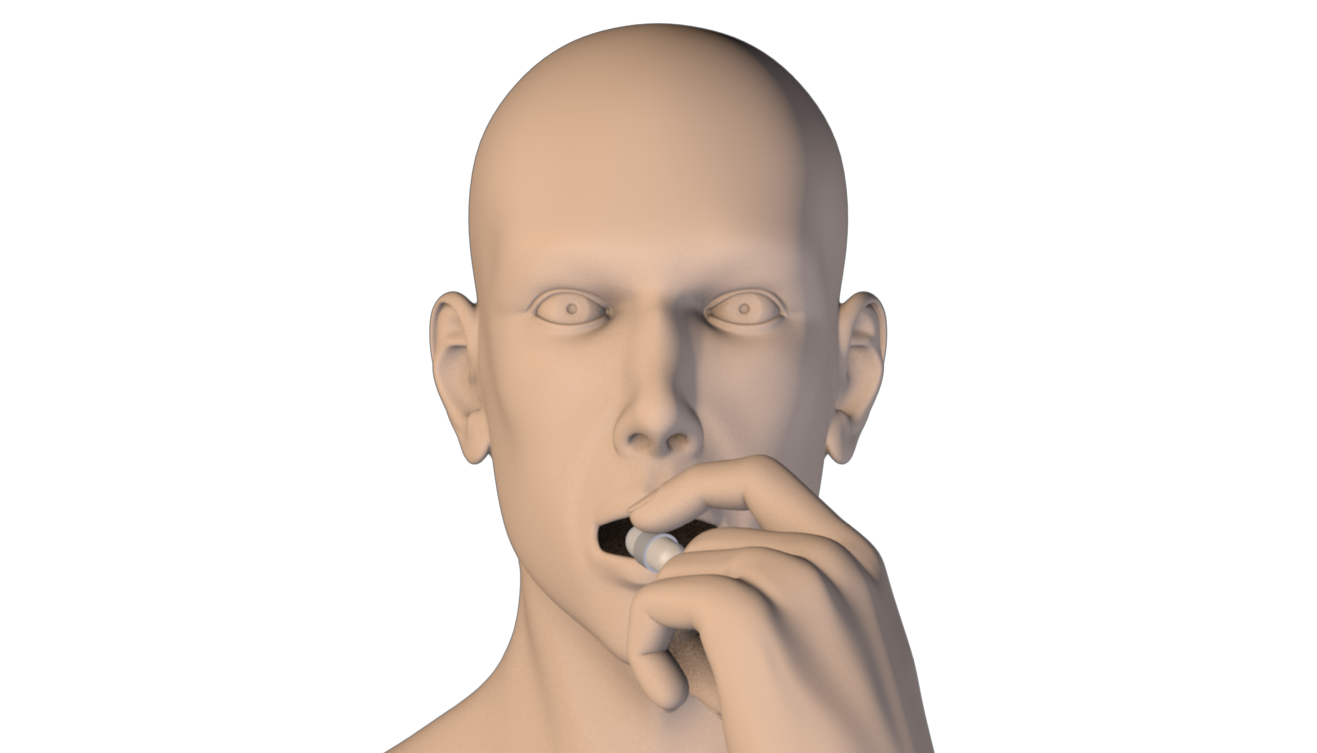
The aim of ROBO-IMPLANT is to develop a fully implantable AP based on a smart non-invasive insulin refilling strategy (through an ingestible pill) and a wireless battery recharging strategy, thus to overcome the limitations of currently available systems.
The ROBO-IMPLANT system guarantees an automatic infusion of insulin at the intraperitoneal level and a non-invasive refilling/recharging strategy, thus assuring: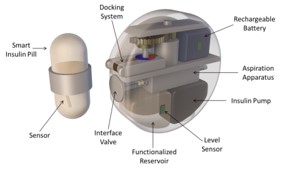
- Optimal glycemic control (with no delays)
- Normal lifestyle restored (ability to perform sport, to swim, etc.)
- Fully disappearing technology and automatic control (diabetic patients would really almost forget their pathology)
- Fully acceptable non-invasive refilling and wireless battery recharging procedure.
The project objective is to develop a full prototype of such a new AP technology and to validate it on a diabetic animal model.
